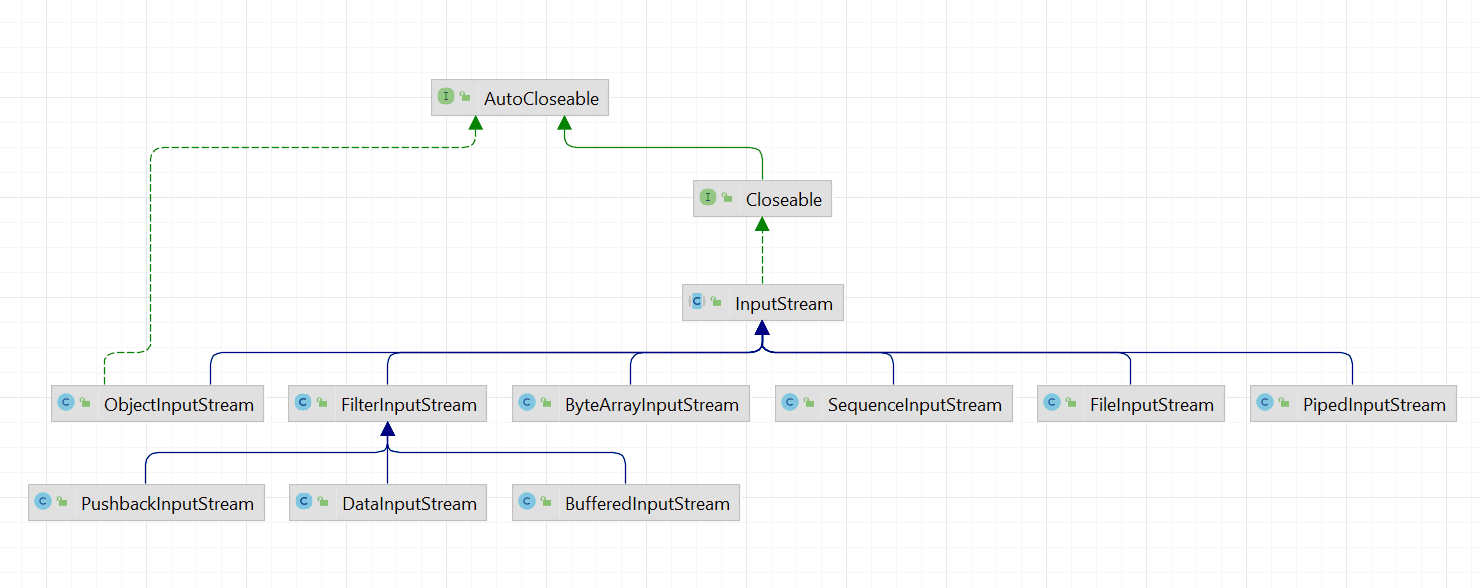
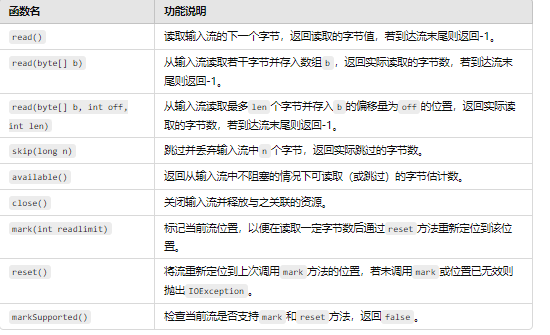
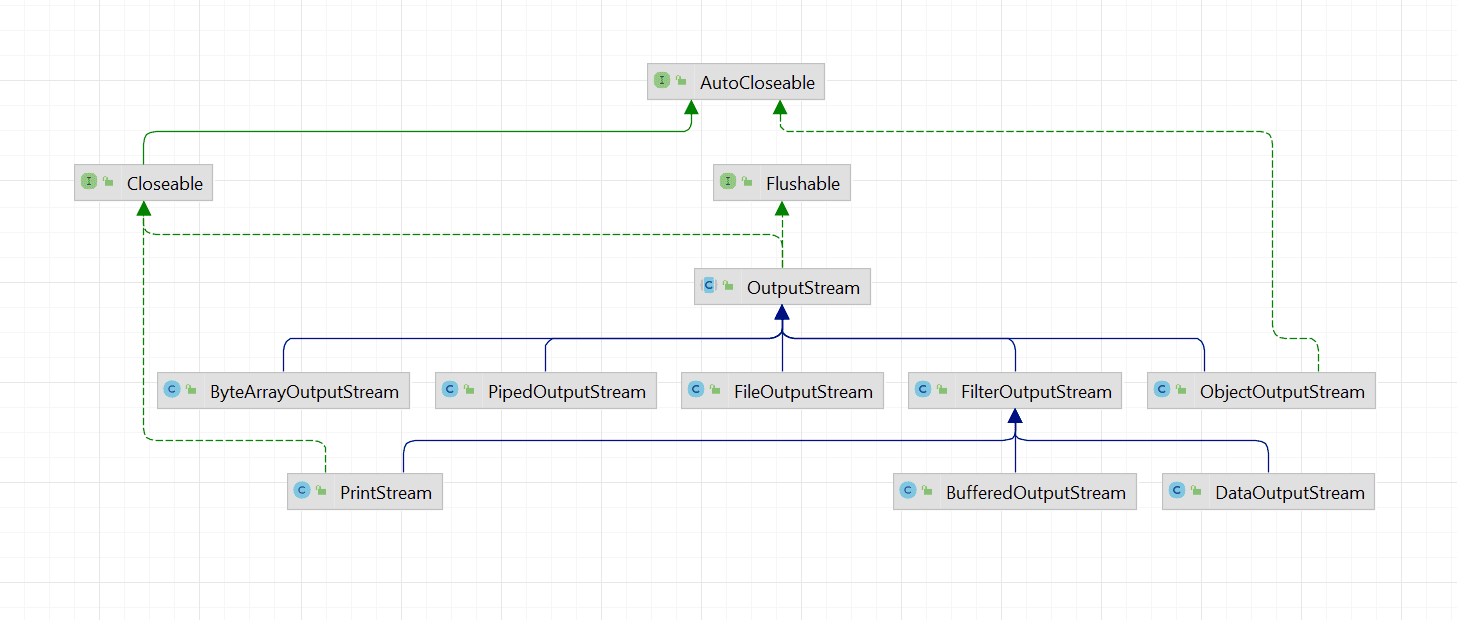
类实现关系
抽象类解读
1 2 public long transferTo (OutputStream out)
源码实现
梳理部分InputStream及其实现类的源码分析。
源码解读-jdk8
https://gitee.com/laomaodu/myinput-stream/blob/master/src/main/java/MyInputStream.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 import java.io.Closeable;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStream;import java.io.OutputStream;import java.util.Objects;public abstract class MyInputStream implements Closeable {private static final int MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE = 2048 ;private static final int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192 ;public abstract int read () throws IOException;public int read (byte b[]) throws IOException {return read(b, 0 , b.length);public int read (byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {if (len == 0 ) {return 0 ;int c = read();if (c == -1 ) { return -1 ;byte )c;int i = 1 ;try {for (; i < len ; i++) {if (c == -1 ) {break ;byte )c;catch (IOException ee) {return i;public long skip (long n) throws IOException {long remaining = n;int nr;if (n <= 0 ) {return 0 ;int size = (int )Math.min(MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE, remaining);byte [] skipBuffer = new byte [size];while (remaining > 0 ) {0 , (int )Math.min(size, remaining));if (nr < 0 ) {break ;return n - remaining;public int available () throws IOException {return 0 ;public void close () throws IOException {}public synchronized void mark (int readlimit) {}public synchronized void reset () throws IOException {throw new IOException ("mark/reset not supported" );public boolean markSupported () {return false ;
2.jdk9更新 1.具体更新 InputStream
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public byte [] readAllBytes()public byte [] readNBytes(int len)public int readNBytes (byte [] b, int off, int len) public long transferTo (OutputStream out) @Native public static final int MAX_VALUE = 0x7fffffff ;
2.空模式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 public static InputStream nullInputStream () {return new InputStream () {private volatile boolean closed;private void ensureOpen () throws IOException {if (closed) {throw new IOException ("Stream closed" );@Override public int available () throws IOException {return 0 ;@Override public int read () throws IOException {return -1 ;@Override public int read (byte [] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {if (len == 0 ) {return 0 ;return -1 ;@Override public byte [] readAllBytes() throws IOException {return new byte [0 ];@Override public int readNBytes (byte [] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {return 0 ;@Override public byte [] readNBytes(int len) throws IOException {if (len < 0 ) {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("len < 0" );return new byte [0 ];@Override public long skip (long n) throws IOException {return 0L ;@Override public long transferTo (OutputStream out) throws IOException {return 0L ;@Override public void close () throws IOException {true ;
3.读取所有字节 1 2 3 4 private static final int MAX_BUFFER_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8 ;
1 2 3 4 5 public byte [] readAllBytes() throws IOException {return readNBytes(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 public byte [] readNBytes(int len) throws IOException {if (len < 0 ) {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("len < 0" );byte []> bufs = null ; byte [] result = null ; int total = 0 ;int remaining = len; int n;do {byte [] buf = new byte [Math.min(remaining, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE)];int nread = 0 ;while ((n = read(buf, nread,0 ) {if (nread > 0 ) {if (MAX_BUFFER_SIZE - total < nread) {throw new OutOfMemoryError ("Required array size too large" );if (result == null ) {else {if (bufs == null ) {new ArrayList <>();while (n >= 0 && remaining > 0 );if (bufs == null ) {if (result == null ) {return new byte [0 ];return result.length == total ?new byte [total];int offset = 0 ;for (byte [] b : bufs) {int count = Math.min(b.length, remaining);0 , result, offset, count);return result;
3.阻塞读取字节保存数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public int readNBytes (byte [] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {int n = 0 ;while (n < len) {int count = read(b, off + n, len - n);if (count < 0 )break ;return n;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public long transferTo (OutputStream out) throws IOException {"out" );long transferred = 0 ;byte [] buffer = new byte [DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE];int read;while ((read = this .read(buffer, 0 , DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE)) >= 0 ) {0 , read);return transferred;
5.总结
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public class TestInputStream {private InputStream inputStream;private static final String CONTENT = "Hello World" ;@Before public void setUp () throws Exception {this .inputStream ="/input.txt" );@Test public void testReadAllBytes () throws Exception {final String content = new String (this .inputStream.readAllBytes());@Test public void testReadNBytes () throws Exception {final byte [] data = new byte [5 ];this .inputStream.readNBytes(data, 0 , 5 );"Hello" , new String (data));@Test public void testTransferTo () throws Exception {final ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream ();this .inputStream.transferTo(outputStream);
通过三种方法验证 InputStream 的读取功能,确保能够正确读取数据并处理流操作。每个测试方法都使用 assertEquals 进行断言,确保期望值与实际值一致。
6.read readnbytes探究 在java中,InputStream类有方法read(byte[], int, int)和readNBytes(byte[], int, int)。看起来这两个方法具有完全相同的功能,所以我想知道它们之间有什么区别。
read()表示它尝试读取*“最多len字节…但可能读取较少的数字 。此方法会阻塞,直到输入数据可用、检测到文件末尾或引发异常。”*readNBytes()说“阻塞直到len读取输入数据的字节,检测到流的末尾,或者抛出异常。”
尽管JDK 的实现 可能会为InputStream这两种方法提供相同的结果,但记录的差异意味着从它继承的其他类可能会表现不同。
例如,给定流'12345<end>',read(s,0,10)允许返回'123',而readNbytes()更有可能继续寻找流的末尾并提供整个内容。
举个例子:如果文本内容是12345<end>, read(s,0,10)是允许返回123的, 而readNbytes(s,0,10)会一直(while循环)查找直到stream尾为止,并返回12345.
7.空对空模式 例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class MyParser implements Parser {private static Action NO_ACTION = new Action () {public void doSomething () { }public Action findAction (String userInput) {if ( ) {return NO_ACTION;
然后便可以始终可以这么调用,而不用再判断空了
1 ParserFactory.getParser().findAction(someInput).doSomething();
在这里,调用者不需要检查返回的 Action 是否为 null。无论如何,调用 doSomething 方法都不会引发 NullPointerException。如果找到了有效的动作,则执行相应的操作;如果没有找到动作,则 doSomething 什么都不做。
3.输入输出缓冲区 如同管道一样
在 Java 的输入输出流实现中,缓冲区 用于在读取和写入数据时提供临时存储,以提高数据传输的效率。skip 方法的设计通过缓冲区实现对输入流字节的跳过,但并不会将这些字节存储在主程序的实际变量中。
输入缓冲区 :这是指从外部数据源(如文件或网络)读取数据时使用的临时存储区域。读取数据时,输入流会将数据批量加载到缓冲区中,而不是逐字节加载,优化了读取速度。
输出缓冲区 :在输出数据(如写入文件或网络)时,数据首先会被存储到缓冲区,然后批量写入目标输出。
在 skip 方法中,skipBuffer 充当了一个 临时输入缓冲区 ,用于存放读取到的字节。这些字节不是直接存储到主程序的内存,而是立即舍弃,从而实现“跳过”的效果。
为什么需要缓冲区
提高效率 :skip 方法不能直接跳过任意数量的字节,尤其是流类型不支持随意定位的情况下。比如在网络流中,不支持直接定位到某个字节位置,因此必须通过逐个读取字节的方式跳过。
批量读取减少 I/O 操作 :skipBuffer 的存在使得方法可以批量读取指定字节数,而不是逐字节读取。相比逐字节读取,这种方式减少了 I/O 操作的次数,提升了性能。
FilterInputStream 源码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public class FilterInputStream extends InputStream {protected volatile InputStream in;protected FilterInputStream (InputStream in) {this .in = in;public int read () throws IOException {return in.read();public int read (byte b[]) throws IOException {return read(b, 0 , b.length);public int read (byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {return in.read(b, off, len);public long skip (long n) throws IOException {return in.skip(n);public int available () throws IOException {return in.available();public void close () throws IOException {public synchronized void mark (int readlimit) {public synchronized void reset () throws IOException {public boolean markSupported () {return in.markSupported();
ByteArrayInputStream源码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 public class ByteArrayInputStream extends InputStream {protected byte buf[];protected int pos;protected int mark = 0 ;protected int count;public ByteArrayInputStream (byte buf[]) {this .buf = buf; this .pos = 0 ;this .count = buf.length;public ByteArrayInputStream (byte buf[], int offset, int length) { this .buf = buf;this .pos = offset;this .count = Math.min(offset + length, buf.length);this .mark = offset;public synchronized int read () {return (pos < count) ? (buf[pos++] & 0xff ) : -1 ;public synchronized int read (byte b[], int off, int len) {if (b == null ) {throw new NullPointerException ();else if (off < 0 || len < 0 || len > b.length - off) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ();if (pos >= count) {return -1 ;int avail = count - pos;if (len > avail) {if (len <= 0 ) {return 0 ;return len;public synchronized long skip (long n) {long k = count - pos;if (n < k) {0 ? 0 : n;return k;public synchronized int available () {return count - pos;public boolean markSupported () { return true ;public void mark (int readAheadLimit) { public synchronized void reset () {public void close () throws IOException {
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 public class BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream {private static int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192 ;private static int MAX_BUFFER_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8 ;protected volatile byte buf[];private static final AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<BufferedInputStream, byte []> bufUpdater =byte [].class, "buf" );protected int count;protected int pos;protected int markpos = -1 ;protected int marklimit;private InputStream getInIfOpen () throws IOException {InputStream input = in;if (input == null )throw new IOException ("Stream closed" );return input;private byte [] getBufIfOpen() throws IOException {byte [] buffer = buf;if (buffer == null )throw new IOException ("Stream closed" );return buffer;public BufferedInputStream (InputStream in) {this (in, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);public BufferedInputStream (InputStream in, int size) {super (in);if (size <= 0 ) {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Buffer size <= 0" );new byte [size];private void fill () throws IOException {byte [] buffer = getBufIfOpen();if (markpos < 0 )0 ; else if (pos >= buffer.length) if (markpos > 0 ) { int sz = pos - markpos;0 , sz);0 ;else if (buffer.length >= marklimit) {1 ; 0 ; else if (buffer.length >= MAX_BUFFER_SIZE) {throw new OutOfMemoryError ("Required array size too large" );else { int nsz = (pos <= MAX_BUFFER_SIZE - pos) ?2 : MAX_BUFFER_SIZE;if (nsz > marklimit)byte nbuf[] = new byte [nsz];0 , nbuf, 0 , pos);if (!bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this , buffer, nbuf)) {throw new IOException ("Stream closed" );int n = getInIfOpen().read(buffer, pos, buffer.length - pos);if (n > 0 )public synchronized int read () throws IOException {if (pos >= count) {if (pos >= count)return -1 ;return getBufIfOpen()[pos++] & 0xff ;private int read1 (byte [] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {int avail = count - pos;if (avail <= 0 ) {if (len >= getBufIfOpen().length && markpos < 0 ) {return getInIfOpen().read(b, off, len);if (avail <= 0 ) return -1 ;int cnt = (avail < len) ? avail : len;return cnt;public synchronized int read (byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOExceptionif ((off | len | (off + len) | (b.length - (off + len))) < 0 ) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ();else if (len == 0 ) {return 0 ;int n = 0 ;for (;;) {int nread = read1(b, off + n, len - n);if (nread <= 0 )return (n == 0 ) ? nread : n;if (n >= len)return n;InputStream input = in;if (input != null && input.available() <= 0 )return n;public synchronized long skip (long n) throws IOException {if (n <= 0 ) {return 0 ;long avail = count - pos;if (avail <= 0 ) {if (markpos <0 )return getInIfOpen().skip(n);if (avail <= 0 )return 0 ;long skipped = (avail < n) ? avail : n;return skipped;public synchronized int available () throws IOException {int n = count - pos;int avail = getInIfOpen().available();return n > (Integer.MAX_VALUE - avail)public synchronized void mark (int readlimit) {public synchronized void reset () throws IOException {if (markpos < 0 )throw new IOException ("Resetting to invalid mark" );public boolean markSupported () {return true ;public void close () throws IOException {byte [] buffer;while ( (buffer = buf) != null ) {if (bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this , buffer, null )) {InputStream input = in;null ;if (input != null )return ;
7.ps 5 6源码没细看,先去过java基础,后续再回来研究喜喜
OutputStream(3)
OutputStream是输出字节流,具体的实现类层次结构如下:
抽象类 OutputStream 类重要方法设计如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public abstract void write (int b) public void write (byte b[]) public void write (byte b[], int off, int len) public void flush () public void close ()
源码实现
梳理部分OutputStream及其实现类的源码分析。
OutputStream抽象类源码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 public abstract class OutputStream implements Closeable , Flushable {public static OutputStream nullOutputStream () {return new OutputStream () {private volatile boolean closed;private void ensureOpen () throws IOException {if (closed) {throw new IOException ("Stream closed" );@Override public void write (int b) throws IOException {@Override public void write (byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {@Override public void close () {true ;public abstract void write (int b) throws IOException;public void write (byte b[]) throws IOException {0 , b.length);public void write (byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {for (int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) {public void flush () throws IOException {public void close () throws IOException {
ps:不读了,嘻嘻。就这丫