Java IO 1
1.传输方式
从数据传输方式或者说是运输方式角度看,可以将 IO 类分为:
字节是个计算机看的,字符才是给人看的
1.字节流
(整体结构如下,部分派生类有缺失)
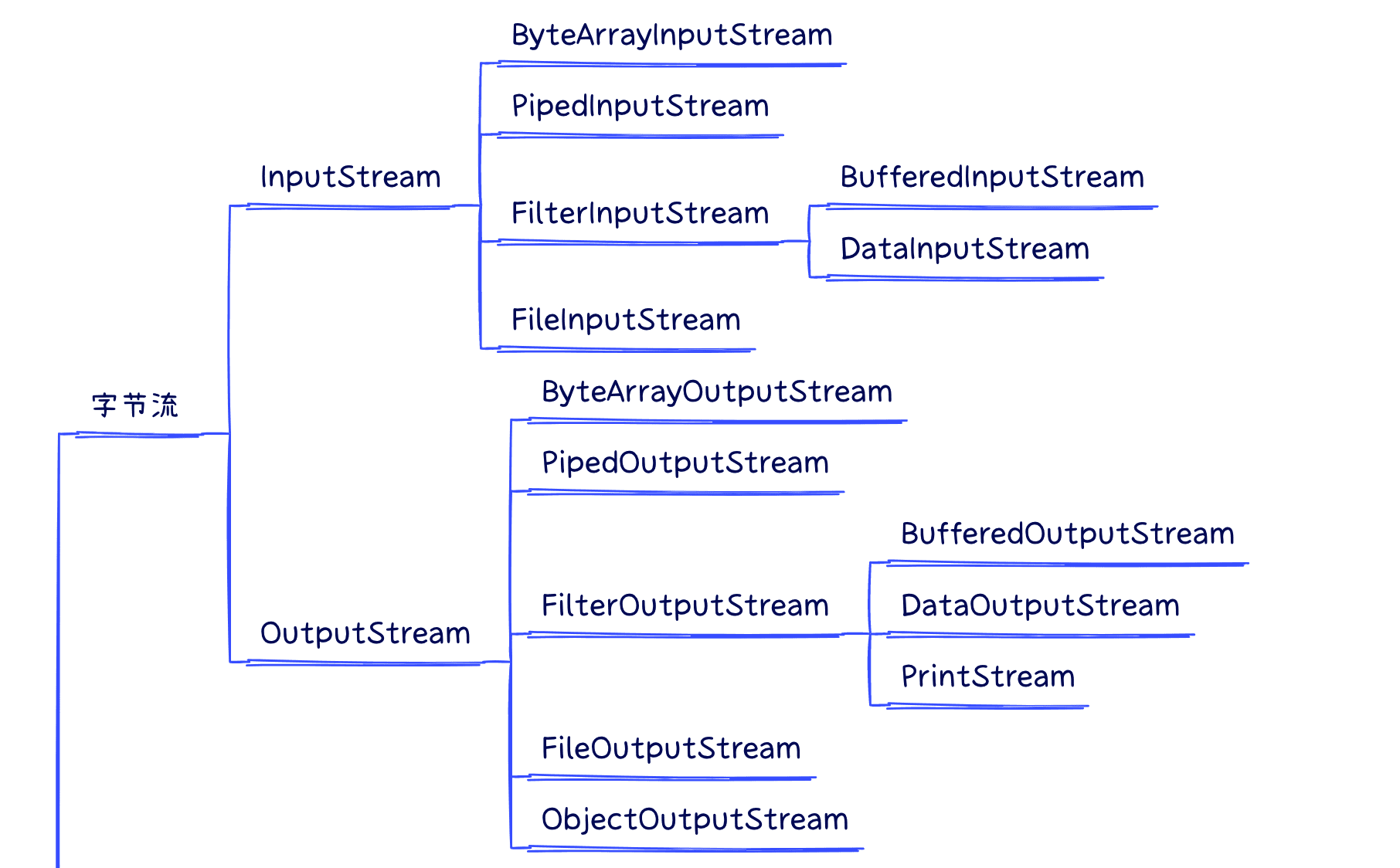
2.字符流
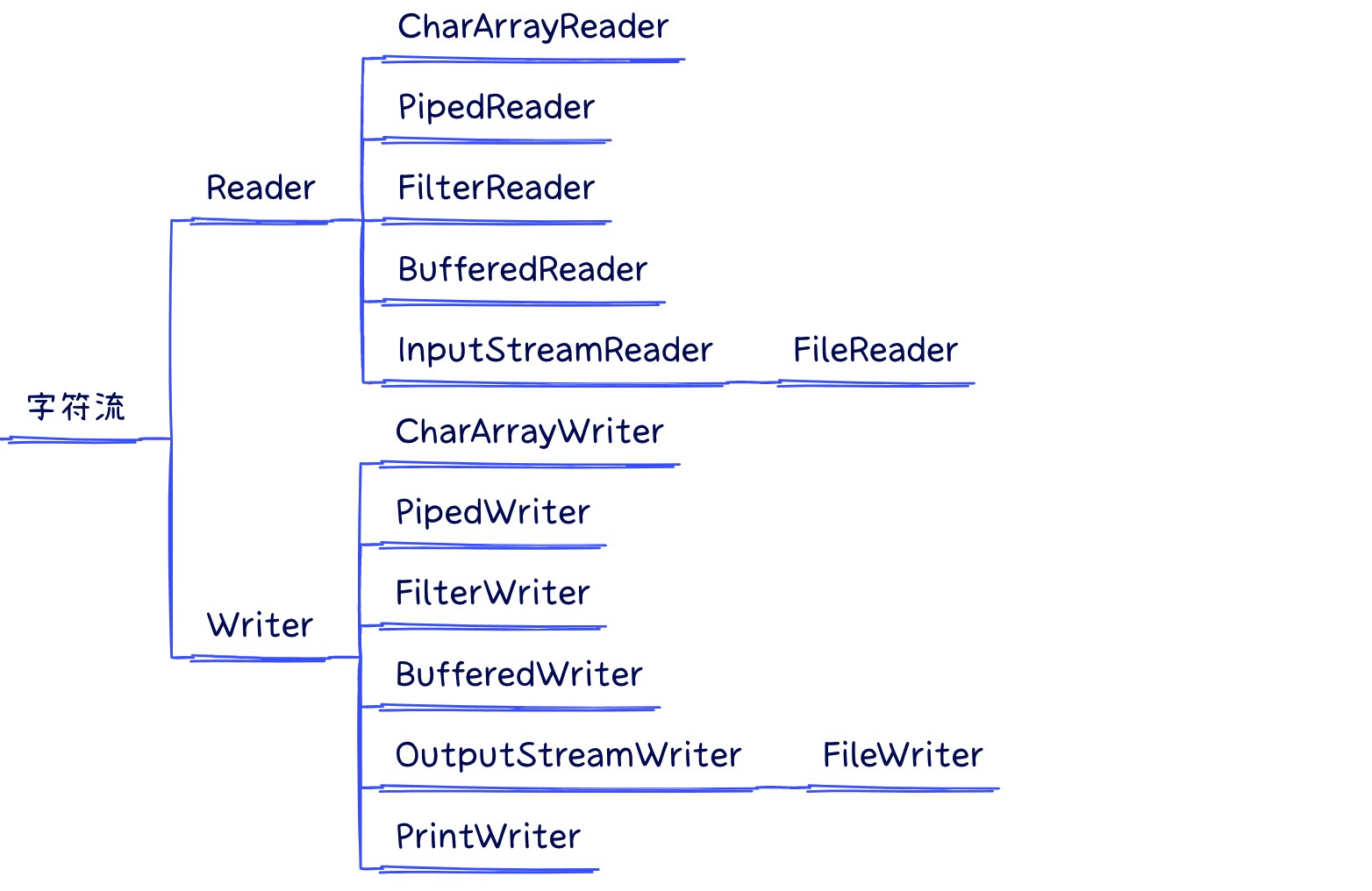
3.区别
字符 读取文件内容-是从字节流到字符流的桥梁,它将字节流转换为字符流。–字符流用来处理文本文件(可以看做是特殊的二进制文件,使用了某种编码,人可以阅读)。
字节 读取图片 视频文件-主要用于读取二进制数据,比如图片、音频、视频等文件。
简而言之,字节是给计算机看的,字符才是给人看的。
4.字节转换
编码就是把字符转换为字节,而解码是把字节重新组合成字符。
如果编码和解码过程使用不同的编码方式那么就出现了乱码。
从字节流转换到字符流
使用InputStreamReader。它读取字节并将它们解码为字符,通常需要指定字符集来进行正确的解码。
1
2
| FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("file.txt");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8");
|
从字符流转换到字节流:
使用OutputStreamWriter。它将字符编码为字节并写入到输出流,通常也需要指定字符集。
1
2
3
| OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("file.txt"), "UTF-8")
osw.write("Hello, World!")
osw.close()
|
2.数据操作
从数据来源或者说是操作对象角度看,IO 类可以分为:
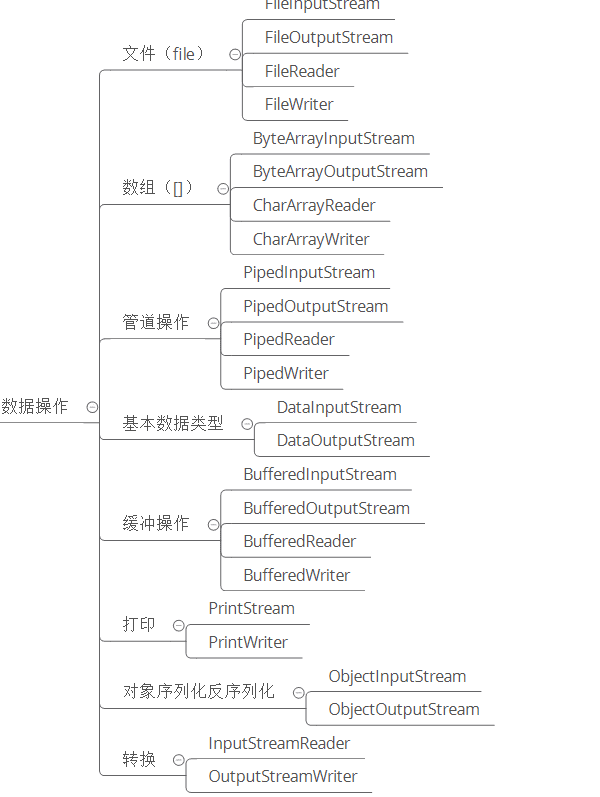
1.文件
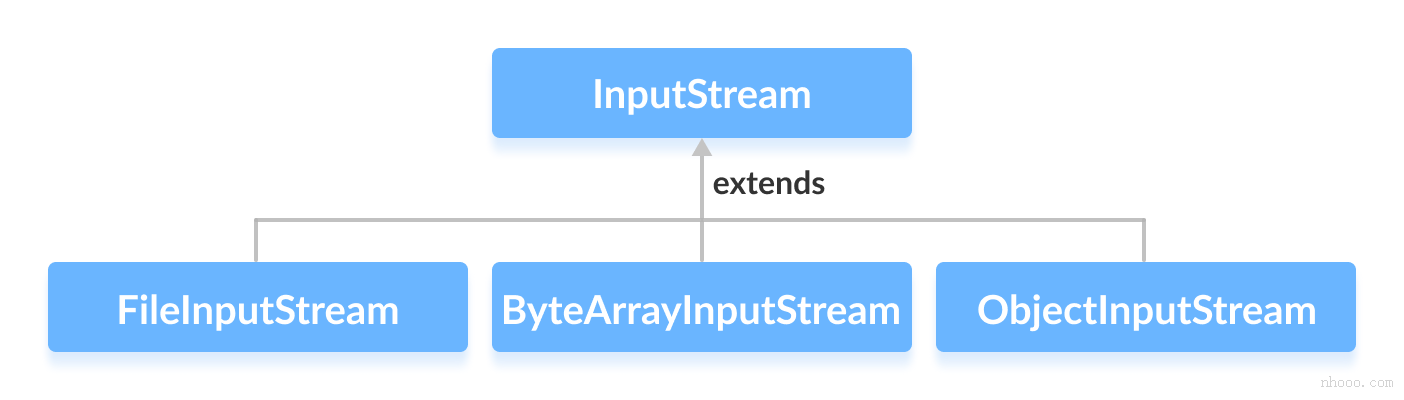
文件读取 -字节读取-序列化读取
1
2
| FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("file.txt");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8");
|
2.outputstream
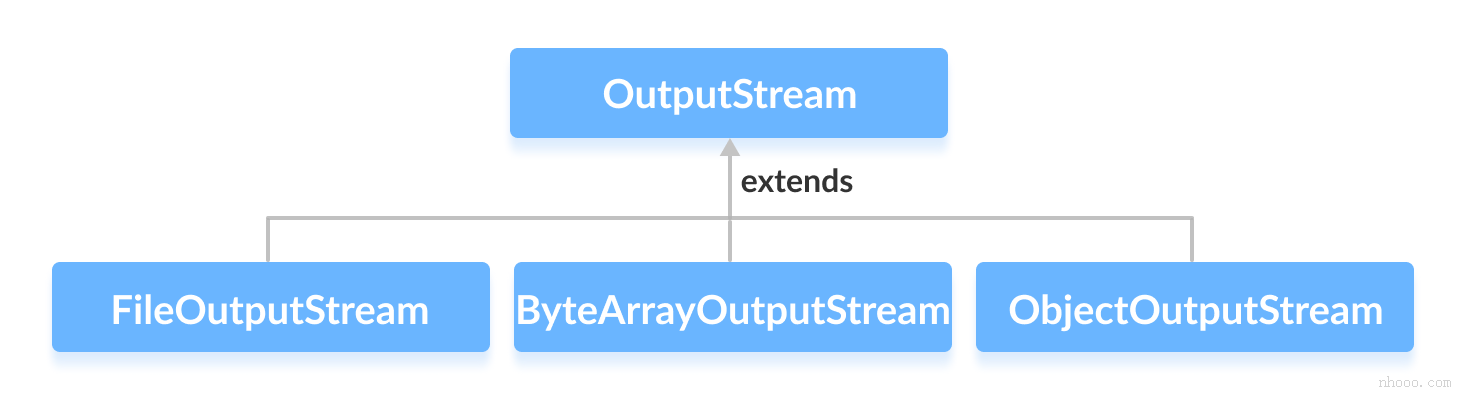
1
2
3
| OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("file.txt"), "UTF-8")
osw.write("Hello, World!")
osw.close()
|
3.writer
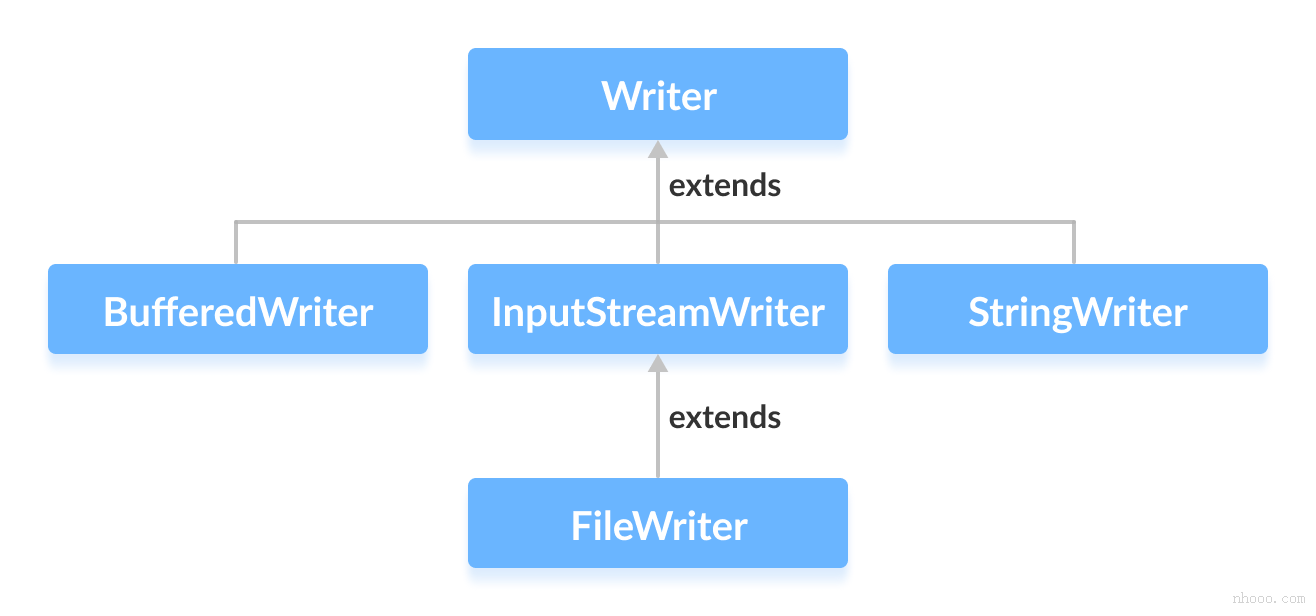
Writer类提供了由其子类实现的不同方法。 以下是一些方法: 字符操作
4.reade
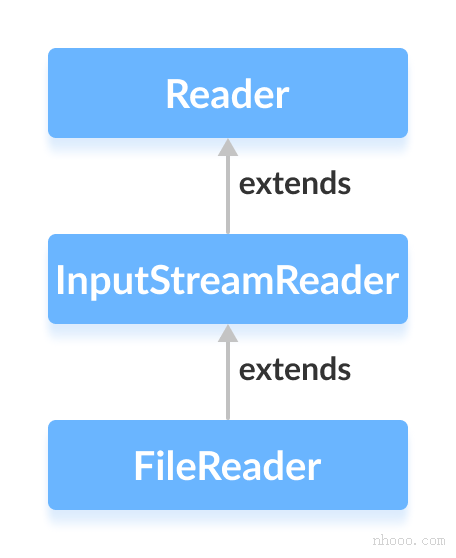
5.小节
不带writer和reade的是字节操作-带的是字符操作
2.数组
字节数组(byte[]): ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream
字符数组(char[]): CharArrayReader、CharArrayWriter
3.管道
PipedInputStream、PipedOutputStream、PipedReader、PipedWriter
4.基本数据类型
DataInputStream、DataOutputStream
5.缓存操作
BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream、BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
6.打印
PrintStream、PrintWriter
7.对象序列化反序列化
ObjectInputStream、ObjectOutputStream
8.转换
inputstreamreader
outputstreamwriter
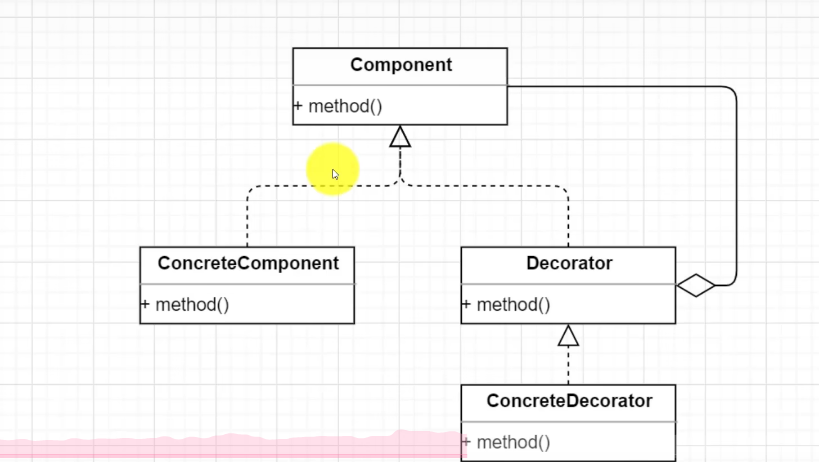
3.装饰者模式
1.了解装饰者模式
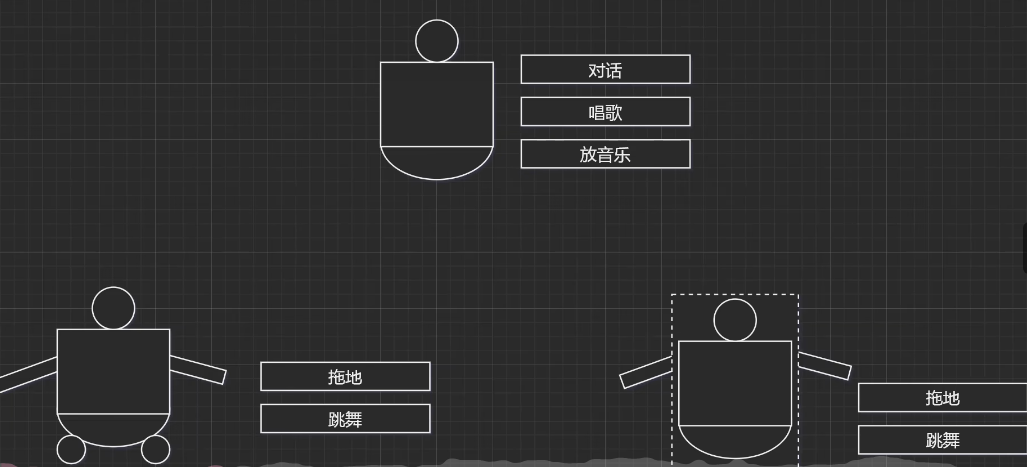
如图-
我们对于机器人两种更新方法功能
1.继承机制
厂商继承第一代研发
2.关联机制-
箱子嵌入以前机器人,我们做研发

类图
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
interface Robota
{
void sayHello();
}
class RobotImpl implements Robota
{
@Override
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("唱歌跳舞");
}
}
abstract class Tirtest implements Robota {
private Robota robot;
public Tirtest(Robota robot) {
this.robot = robot;
}
@Override
public void sayHello() {
robot.sayHello();
}
public void saypp()
{
robot.sayHello();
System.out.println("pp");
}
}
class test extends Tirtest{
public test(Robota robot) {
super(robot);
}
}
public class decorator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Robota robot = new RobotImpl();
test t = new test(robot);
t.saypp();
}
}
|
装饰器模式是在原有类的基础上动态添加新的功能,这种添加功能的方式不同于继承,它是在对象层面实现功能扩展,而不是继承的类层面,因此说装饰器模式比继承更加灵活。另外,装饰器模式属于结构型设计模式。之前讲的都是创建型设计模式。创建型可以理解为生成新的对象,而结构型可以理解为构建更大的类或类对象。
InputStream 是抽象组件;
FileInputStream 是 InputStream 的子类,属于具体组件,提供了字节流的输入操作;
FilterInputStream 属于抽象装饰者,装饰者用于装饰组件,为组件提供额外的功能。例如 BufferedInputStream 为 FileInputStream 提供缓存的功能。
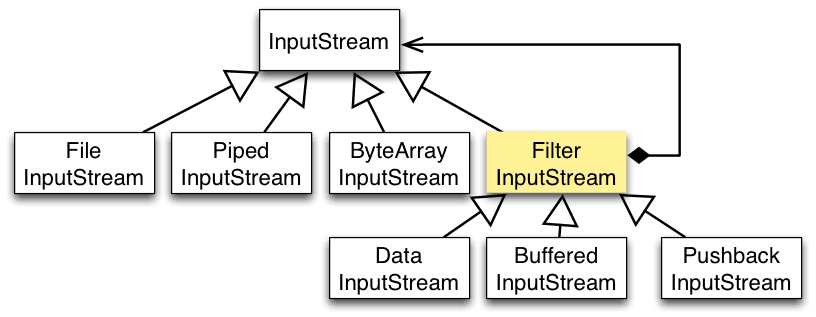
实例化一个具有缓存功能的字节流对象时,只需要在 FileInputStream 对象上再套一层 BufferedInputStream 对象即可。
1
| FileInputStream fileInputStream =newFileInputStream(filePath)
|
DataInputStream 装饰者提供了对更多数据类型进行输入的操作,比如 int、double 等基本类型。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
interface inputStreama
{
void sayHello();
}
class FileInputStreama implements inputStreama
{
@Override
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("文件操作");
}
}
abstract class FilterInputStreamq implements inputStreama {
private inputStreama robot;
public FilterInputStreamq(inputStreama robot) {
this.robot = robot;
}
@Override
public void sayHello() {
robot.sayHello();
}
public void saypp()
{
robot.sayHello();
System.out.println("文件传输增强");
}
}
class test extends FilterInputStreamq {
public test(inputStreama robot) {
super(robot);
}
}
public class decorator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
inputStreama robot = new FileInputStreama();
test t = new test(robot);
t.saypp();
}
}
|
4.常见类的使用
本文主要介绍Java IO常见类的使用,包括:磁盘操作,字节操作,字符操作,对象操作和网络操作。

IO常见类
file相关
File 类可以用于表示文件和目录的信息,但是它不表示文件的内容。
递归地列出一个目录下所有文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public static void listAllFiles(File dir) {
if (dir == null || !dir.exists()) {
return;
}
if (dir.isFile()) {
System.out.println(dir.getName());
return;
}
for (File file : dir.listFiles()) {
listAllFiles(file);
}
}
|
字节流相关
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public static void copyFile(String src, String dist) throws IOException {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(src);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dist);
byte[] buffer = new byte[20 * 1024];
while (in.read(buffer, 0, buffer.length) != -1) {
out.write(buffer);
}
in.close();
out.close();
}
|
实现逐行输出文本文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public static void readFileContent(String filePath) throws IOException {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
String line;
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
bufferedReader.close();
}
|
序列化 Serializable & transient
序列化就是将一个对象转换成字节序列,方便存储和传输。
- 序列化: ObjectOutputStream.writeObject()
- 反序列化: ObjectInputStream.readObject()
不会对静态变量进行序列化,因为序列化只是保存对象的状态,静态变量属于类的状态。
Serializable
序列化的类需要实现 Serializable 接口,它只是一个标准,没有任何方法需要实现,但是如果不去实现它的话而进行序列化,会抛出异常。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
A a1 = new A(123, "abc");
String objectFile = "file/a1";
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(objectFile));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(a1);
objectOutputStream.close();
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(objectFile));
A a2 = (A) objectInputStream.readObject();
objectInputStream.close();
System.out.println(a2);
}
private static class A implements Serializable {
private int x;
private String y;
A(int x, String y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "x = " + x + " " + "y = " + y;
}
}
|
transient
transient 关键字可以使一些属性不会被序列化。
ArrayList 中存储数据的数组 elementData 是用 transient 修饰的,因为这个数组是动态扩展的,并不是所有的空间都被使用,因此就不需要所有的内容都被序列化。通过重写序列化和反序列化方法,使得可以只序列化数组中有内容的那部分数据。
1
2
| private transient Object[] elementData;
|
java网络支持

inetAdress
没有公有的构造函数,只能通过静态方法来创建实例。
1
2
| InetAddress.getByName(String host);
InetAddress.getByAddress(byte[] address);
|
url
可以直接从 URL 中读取字节流数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
URL url = new URL("http://www.baidu.com");
InputStream is = url.openStream();
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is, "utf-8");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}
|
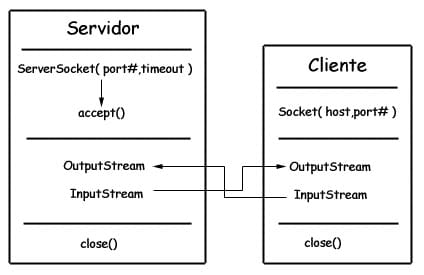
sockets
- ServerSocket: 服务器端类
- Socket: 客户端类
- 服务器和客户端通过 InputStream 和 OutputStream 进行输入输出。
datagram
- DatagramSocket: 通信类
- DatagramPacket: 数据包类













